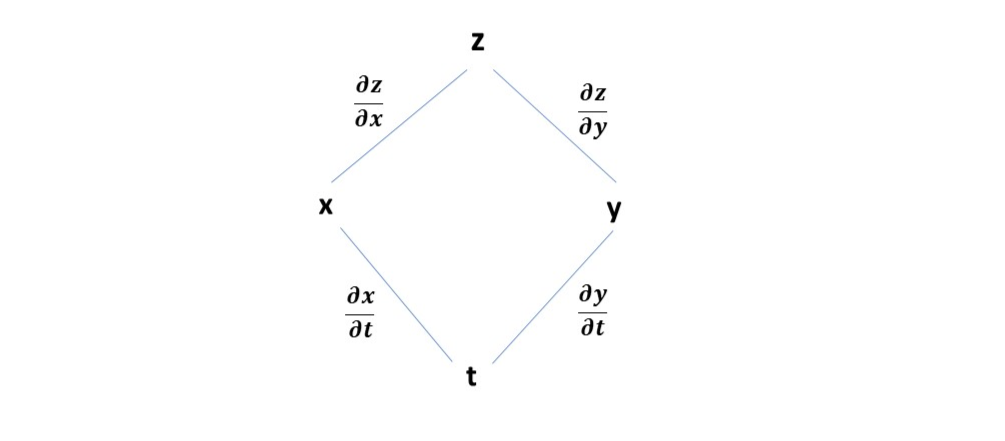
A chain rule dependency diagram is useful for calculating more involved partial differentiations using chain rule.
To draw a diagram for , start from the initial function/variable, say , which is defined in terms of undesired variables (say and ). The diagram starts with as the first node. Add the variables as children to the current variable’s node. Do this repeatedly to all the newly added child nodes (leaves) until they reach at the desired variable ( in this case). Each edge in the diagram represents a partial derivative ( where is the parent variable and is child variable). For each possible path from the initial to the desired variable ( to ), multiply all the edges (e.g. -- becomes ). Sum all the paths together to get the desired partial differentiation (e.g. ).